Table of Contents
- What is e-Invoicing?
- Types of e-Invoices in Malaysia
- What are the Transaction Types Covered Under e-Invoicing?
- What are the Benefits of e-Invoicing?
- What is the e-Invoice Implementation Timeline
- In What Scenarios Do e-Invoices Need to Be Issued
- How to Submit an e-Invoice in Malaysia
- Who Needs to Comply With e-Invoicing?
- What Are My Data Integration Options for e-Invoicing?
- VeecoTech Middleware: The Hassle-Free Solution for e-Invoicing
- FAQ
e-Invoicing in Malaysia: What You Need to Know (2024 Guide)
Have you heard the word on the street? All Malaysian companies will soon need to implement e-Invoicing!
It’s part of the Government’s initiative to increase the efficiency of Malaysia’s tax administration management. We’ll start to see these changes starting from 1st August 2024.
So make sure your company stays compliant, by keeping pace with these changes. From the implementation timeline to a step-by-step workflow, learn all the essentials in this complete guide.
What is e-Invoicing?
First things first, e-Invoicing is a digital representation of a transaction between a supplier and a buyer. It replaces traditional paper documents or electronic documents, such as invoices, credit notes, and debit notes.This format allows the invoice data to be processed electronically and automatically.
This structured electronic invoice contains all the data from the supplier, such as supplier and buyer details, item description, and quantity, in a machine-readable format. This data can be automatically transferred into the buyers account payable (AP) system, removing the need for manual entry.
This quality sets it apart from paper invoices and digital forms of invoices (e.g., PDFs, images) which need to be manually viewed and manually entered into AP systems. In fact, e-Invoices do not include a visual representation of the data (although they can be rendered or transposed into visual forms if needed).
The graphic below by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), also known as Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN), perfectly summarises what is and isn’t an e-Invoice: 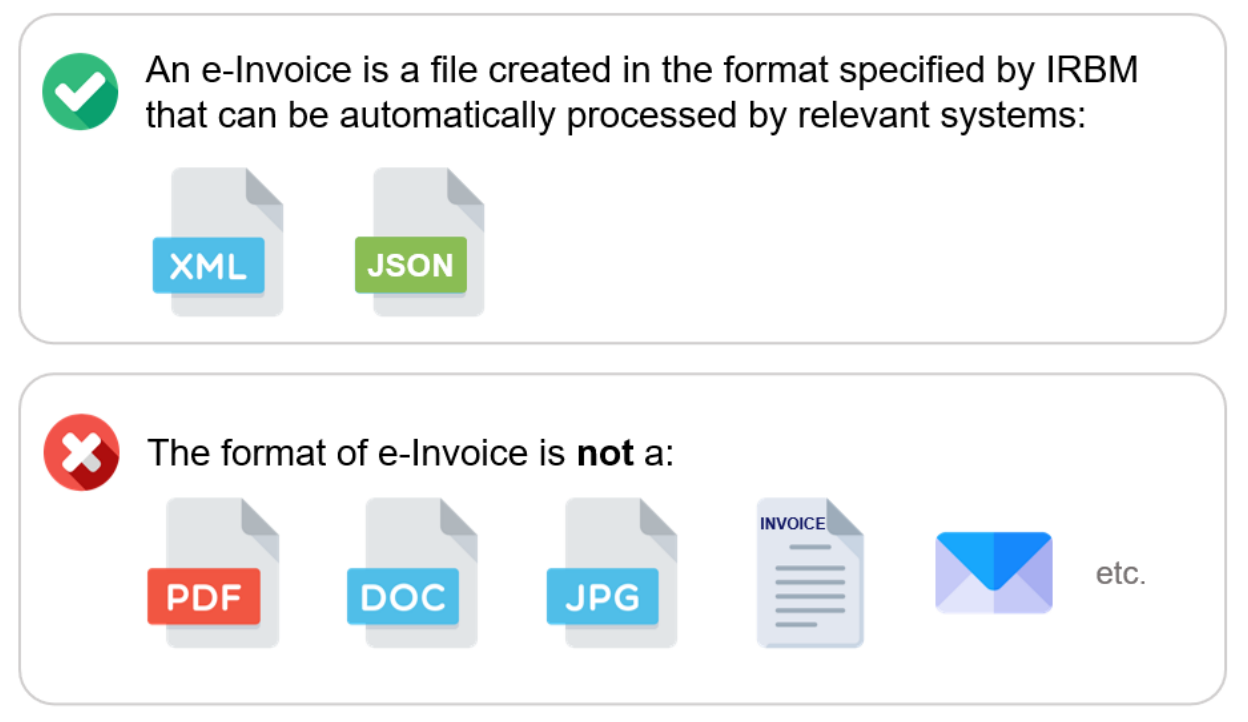
Types of e-Invoices in Malaysia
Here are a few types of e-Invoices to be issued in Malaysia:
- Invoices: A document detailing a transaction between a supplier and buyer, including self-billed e-Invoice to record an expense.
- Credit notes: A document issued by suppliers to correct errors, apply discounts, or record returns – to reduce the value of a previously issued e-invoice (in situations where money is not returned to the buyer).
- Debit notes: A document used to record additional charges on a previously issued e-Invoice.
- Refund notes: A document issued by suppliers to validate the refund of a buyer’s payment (in situations where money is returned to the buyer).
What are the Transaction Types Covered Under e-Invoicing?
e-Invoicing covers transition types such as:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): Transactions, interactions, or relationships from a business to the end consumer.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Transactions, interactions, or relationships from a business to another business(es).
- Business-to-Government (B2G): Commercial transactions from business to government entities.
What are the Benefits of e-Invoicing?
At its core, e-Invoicing helps businesses to improve efficiency and increase tax compliance. Curious to know how exactly e-Invoicing will benefit you? We’ve listed the overall benefits down below:
- Reduce Manual Efforts and Human Errors: Forms a united invoicing process through the creation and submission of transaction documents electronically and automatically to IRBM.
- Facilitate Tax Return Filing: Integrates with systems seamlessly to achieve efficient and accurate tax reporting.
- Streamlines Operations: Automates processes, integrates data seamlessly, and improves invoice management, thus increasing efficiency, and saving time and costs for larger businesses.
- Digitalised Tax and Financial Reporting: Phased implementation supports MSMEs in gradually transitioning to digitalised tax and financial reporting, according to industry standards.
What is the e-Invoice Implementation Timeline
To ensure a smooth transition, e-Invoice will be implemented in several phases. The table below shows the implementation timeline:
| Implementation Date* | Targeted Taxpayers |
|---|---|
| 1 August 2024 | Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM100 million. |
| 1 January 2025 | Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of more than RM25 million and up to RM100 million. |
| 1 July 2025 | All other taxpayers. |
*Note: Taxpayers can choose to voluntarily implement e-Invoice earlier than the mentioned dates.
In What Scenarios Do e-Invoices Need to Be Issued
Businesses will need to issue e-Invoices in the following scenarios:
| No. | Scenario | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Proof of Income | Issued whenever a transaction (e.g., sale) is done to verify the income of taxpayers. |
| 2 | Proof of Expense | Issued as evidence of spending (e.g., purchases, returns, discounts) by taxpayers. It can also be used to adjust (correct or subtract) the amounts documented in an income receipt.
*Note: In certain situations, taxpayers may also need to issue a self-billed e-Invoice to record an expense. |
How to Submit an e-Invoice in Malaysia
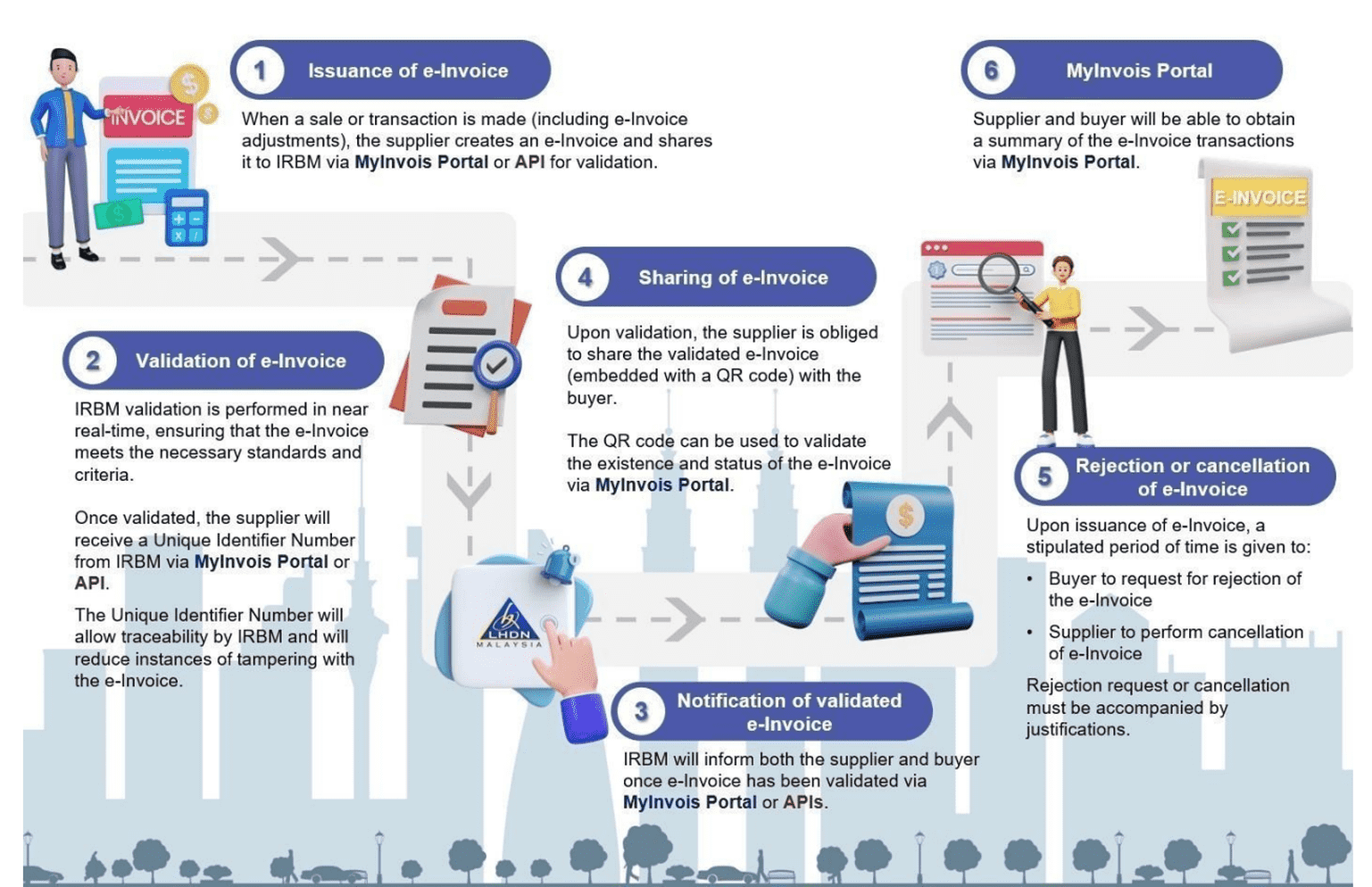
Source: Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM)
Do note that this entire e-Invoice workflow is done via MyInvois Portal and / or API. Here’s a quick rundown of how this process works:
Step 1 – Issuance of e-Invoice: The supplier creates an e-Invoice to document a sale or transaction. Then, they send the e-Invoice to IRBM via MyInvois Portal or API for validation.
Step 2 – Validation of e-Invoice: IRBM performs the validation in near-real time. If the e-Invoice passes the required standards and criteria, the supplier will receive a Unique Identifier Number from IRBM via MyInvois Portal or API.
Step 3 – Notification of Validated e-Invoice: The supplier and buyer will be notified by IRBM via MyInvois Portal or API once the e-Invoice has been validated.
Step 4 – Sharing of e-Invoice: The supplier needs to share the validated e-Invoice, which is embedded with a QR code, with the buyer. This QR code allows them to validate the existence and status of the e-Invoice via MyInvois Portal.
Step 5 – Rejection or Cancellation of e-Invoice: A stipulated time frame is given for the buyer to request for e-Invoice rejection, and the supplier to cancel the e-Invoice.
Step 6 – MyInvois Portal: The supplier and buyer can view a summary of the e-Invoice transactions on the MyInvois Portal.
Who Needs to Comply With e-Invoicing?
In Malaysia, all taxpayers who are conducting commercial activities in the country are required to make e-Invoices. Here is a list of individuals and legal entities who are required to comply OR are exempted from e-Invoicing:
| Required to Comply | Exempted* |
|---|---|
| 1. Associations | 1. Ruler and Ruling Chief |
| 2. Body of persons | 2. Former Ruler and Ruling Chief |
| 3. Branches | 3. Consort of a Ruler of a State |
| 4. Business trusts | 4. Consort of a Former Ruler of a State |
| 5. Co-operative societies | 5. Government |
| 6. Corporations | 6. State government and state authority |
| 7. Limited liability partnerships | 7. Government authority |
| 8. Partnerships | 8. Local authority |
| 9. Property trust funds | 9. Statutory authority and statutory body |
| 10. Property trusts | 10. Facilities provided by the above government, authority, or body |
| 11. Real estate investment trusts | 11. Consular offices and diplomatic officers, consular officers and consular employees |
| 12. Representative offices and regional offices | 12. Individual who is not conducting business |
| 13. Trust bodies | 13. Small traders with sales below RM150,000 (e.g., hawker stalls, roadside stalls) |
| 14. Unit trusts |
*Note 1: Any entities, such as companies and limited liability partnerships, owned by these persons are still required to implement e-Invoice.
*Note 2: An e-Invoice is not required for these types of income or expenses: (1) employment income pension, (2) alimony, (3) distribution of dividend in specific circumstances, and (4) zakat.
What Are My Data Integration Options for e-Invoicing?
Here are three e-Invoice integration options to consider:
| No. | Mechanism | Key Features | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
MyInvois Portal hosted by IRBM |
OR
|
|
| 2 | Application Programming Interface (API) |
|
|
| 3 | Middleware |
|
|
VeecoTech Middleware: The Hassle-Free Solution for e-Invoicing
We hope this article provided useful insights into Malaysia’s e-Invoicing initiative! From this overview, it’s clear that e-Invoices will help local businesses simplify invoicing processes and increase efficiency in the long run.
However, implementing a new system can be resource-intensive and time consuming. From keeping the business running during these changes to experiencing poor support and training, businesses face a variety of challenges in choosing and executing the right transmission mechanism or integration.
Here is where VeecoTech’s middleware solution comes in. We make the implementation process a breeze, ensuring business runs as usual.
VeecoTech, an MDEC-approved Digital Provider since 2022, is a leading software development agency based in Malaysia and Singapore. We specialise in a wide range of services, including website design and development, search engine optimisation (SEO), and e-commerce solutions.
Why Choose VeecoTech Middleware?
- Intelligent Retry Mechanism: Automatically retries if the initial attempt to connect with IRBM fails, ensuring your invoices are submitted without the need for manual intervention.
- 100% IRBM Compliance: Updates regularly and automatically to reflect new compliance standards.
- User-Friendly Login Interface: Features a user-friendly interface for accessing and managing your invoice tasks, designed for individuals of any skill level.
- IRBM Recommended Invoice Format: Allows you to download invoices in the IRBM recommended format, consisting of all 55 required fields (as of 28th June 2024), directly from our system.
- Authorised Digital Certificate & Signature: Ensures every invoice submitted has a mandatory unique digital signature, as VeecoTech is an MDEC-appointed Licensed Certification Authority.
- Integration with ERP system: Integrates smoothly with your existing ERP system, synchronising invoicing data, enhancing operational efficiency, and maintaining accurate financial records.
- Reporting Capabilities: Provides detailed insights into your invoicing operations.
- Continuous Support: VeecoTech provides continuous support pre and post implementation of the middleware, maintaining and resolving any issues with the system.
FAQ
What is the meaning of e-Invoicing?
e-Invoicing is a digital representation of a transaction between a supplier and buyer. This electronic invoice document is transmitted in a structured data format (e.g., XML, JSON).
This format allows information to be processed automatically and electronically. Do note that digital forms of invoices such as PDFs and JPGs are not e-Invoices.
Learn more about what e-Invoicing is in this section.
Is e-Invoicing mandatory for Malaysia?
Yes. By 1st July 2025, all taxpayers in Malaysia that are involved in commercial activities must implement e-invoicing.
Learn more about the implementation timeline in this section.
Who is the e-Invoice authority in Malaysia?
e-Invoice activities are overseen by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM), also known as the Lembaga Hasil Dalam Negeri (LHDN).
Can taxpayers continue claiming tax deduction / personal tax relief without an e-Invoice?
Yes, taxpayers can continue to claim tax deductions and personal tax relief with existing documents until the mandatory implementation period.
Does e-Invoice only apply to transactions in Malaysia?
No, e-Invoice applies to both transactions in Malaysia and cross-border transactions.
Why do we use e-Invoicing?
e-Invoicing is part of the Government’s efforts to increase the efficiency of Malaysia’s tax administration management. Businesses will use e-invoicing to streamline operations and improve tax compliance.
Learn more about the benefits of e-Invoicing in this section.
What is the process of e-Invoicing?
In the Malaysian context, e-Invoicing is a 6 step process:
- Issuance of e-Invoice
- Validation of e-Invoice
- Notification of validated e-Invoice
- Sharing of e-Invoice
- Rejection or cancellation of e-Invoice
- MyInvois Portal
Learn more about the process in this section.
Who needs to make an e-Invoice?
In the Malaysian context, all taxpayers (suppliers) conducting commercial activities in the country need to make e-Invoices.
Learn who is required to comply OR exempted in this section.
How many types of e-Invoice are there?
There are four types of e-Invoices: invoices, credit notes, debit notes, and refund notes.
Learn more about these e-Invoice types in this section.











Leave A Comment